Researchers from the Laboratory for Mechatronics, Production Systems, and Automation have developed an autonomous production unit that, utilizing blockchain technology, independently conducts business transactions, fulfills orders, and manages operations without human intervention. This fully autonomous unit enables flexible, secure, and cost-effective manufacturing, opening up new possibilities for a sustainable and globally connected industry of the future.
Modern manufacturing is increasingly facing the need for greater flexibility, faster responsiveness, and more efficient resource utilization. At the same time, the global distribution of production capacities raises questions of trust, control, and organizational complexity. Traditional systems rely on centralized management, which often limits the autonomy of individual production units. Most existing solutions that aim to enhance the autonomy of production units utilize digital twins and intelligent agent systems; however, decisions are still tied to central business systems, which restrict the independent operation of machines. Thus, the question of whether a completely autonomous production unit capable of independently conducting business, making agreements, and providing manufacturing services is possible has remained open.
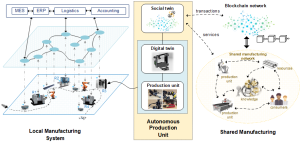
Researchers at the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, University of Ljubljana, have developed an architecture for an autonomous production unit that operates within a global shared manufacturing system based on blockchain technology. This unit independently accepts orders, negotiates terms, provides services, keeps records, and receives payments — all without intermediaries. A key component is the combination of a digital twin and a so-called “social twin,” which allows the unit to understand both the physical and economic environment. The concept was experimentally tested using a 3D printer. The results were published in the journal Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing (Impact Factor = 11.4).
“The proposed concept extends the level of automation of individual production machines, significantly enhancing their capabilities for autonomous operation,” emphasizes the lead author of the study. The research paves the way for the development of globally connected and fully autonomous manufacturing systems, which could play a key role in the future of sustainable industry.
